Base64 Encoder Decoder Ultimate Guide: Complete Tutorial for Web Developers 2025
Master Base64 encoding and decoding with our comprehensive guide. Learn everything about Base64 format, practical use cases, security considerations, and best practices for web development and data transmission.
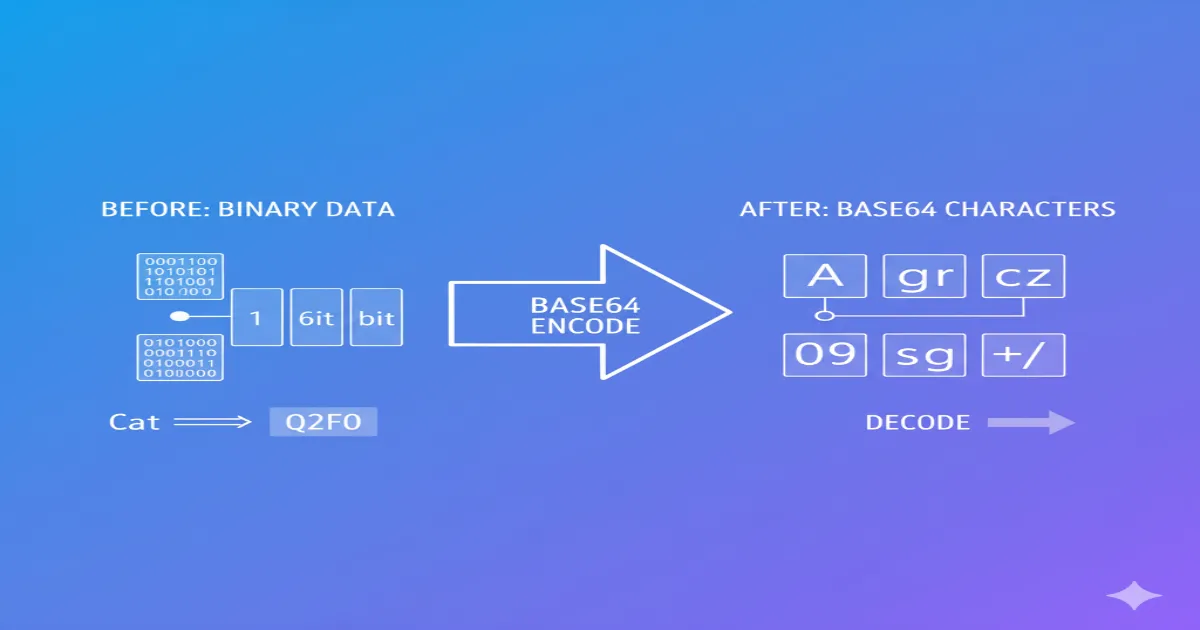
What is Base64 Encoding?
Base64 encoding is a binary-to-text encoding scheme that represents binary data using 64 printable ASCII characters. It's essential for web developers who need to transmit binary data over text-based protocols or embed binary content in text formats.
Our Base64 Encoder/Decoder provides instant, secure encoding and decoding capabilities for all your development needs.
How Base64 Encoding Works
Understanding the Base64 algorithm helps developers make informed decisions about when and how to use it:
Base64 Encoding Process:
- Input Processing: Takes 3 bytes (24 bits) of binary data
- Bit Grouping: Divides into four 6-bit groups
- Character Mapping: Maps each 6-bit group to Base64 character set
- Padding: Adds '=' characters for data alignment if needed
- Output: Produces ASCII text representation
Base64 Character Set
The Base64 alphabet uses 64 characters:
- A-Z: Uppercase letters (indices 0-25)
- a-z: Lowercase letters (indices 26-51)
- 0-9: Digits (indices 52-61)
- + and /: Special characters (indices 62-63)
- =: Padding character
Common Use Cases for Base64 Encoding
Base64 encoding serves many practical purposes in web development and data transmission:
1. Data URLs and Embedded Images
Embed images directly in HTML or CSS without separate file requests:
data:image/png;base64,iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAAAEAAAABCAYAAAAfFcSJAAAADUlEQVR42mNkYPhfDwAChwGA60e6kgAAAABJRU5ErkJggg==
2. API Data Transmission
Send binary files through JSON APIs that only support text data.
3. Email Attachments (MIME)
Email protocols use Base64 to encode binary attachments for transmission.
4. Database Storage
Store binary data in text-only database fields when BLOB support isn't available.
Pro Developer Tip
Use Base64 for small images (icons, logos) to reduce HTTP requests, but serve larger images as separate files to avoid bloating your HTML/CSS files.
Base64 in Different Programming Languages
Most programming languages provide built-in Base64 support:
JavaScript
// Encoding
const encoded = btoa("Hello World");
console.log(encoded); // SGVsbG8gV29ybGQ=
// Decoding
const decoded = atob(encoded);
console.log(decoded); // Hello WorldPython
import base64
# Encoding
message = "Hello World"
encoded = base64.b64encode(message.encode('utf-8'))
print(encoded.decode('utf-8')) # SGVsbG8gV29ybGQ=
# Decoding
decoded = base64.b64decode(encoded)
print(decoded.decode('utf-8')) # Hello WorldPHP
// Encoding
$encoded = base64_encode("Hello World");
echo $encoded; // SGVsbG8gV29ybGQ=
// Decoding
$decoded = base64_decode($encoded);
echo $decoded; // Hello WorldSecurity Considerations and Best Practices
Base64 encoding is NOT encryption or security - it's important to understand its limitations:
Critical Security Warning:
- Base64 is NOT encryption: Anyone can easily decode Base64 data
- Never store passwords: Base64 encoded passwords offer zero security
- Not for sensitive data: Use proper encryption for confidential information
- Reversible encoding: Base64 is designed to be easily decoded
When to Use Base64
Appropriate Use Cases:
- Data format conversion (binary to text)
- Embedding small images in CSS/HTML
- API data transmission where binary isn't supported
- Email attachment encoding (MIME standard)
- URL-safe data transmission (with URL-safe variant)
When NOT to Use Base64
- Large file storage (increases size by 33%)
- Security or encryption needs
- When binary transmission is already supported
- Password storage or authentication tokens
Base64 Variants and Alternatives
Different Base64 implementations serve specific use cases:
Standard vs URL-Safe Base64
Character Differences:
- Standard Base64: Uses + and / (can break in URLs)
- URL-Safe Base64: Uses - and _ (safe for URLs and filenames)
- Padding: Standard uses =, URL-safe may omit padding
Other Encoding Methods
- Base32: More human-readable, case-insensitive
- Hex Encoding: Uses 0-9 and A-F characters only
- URL Encoding: Percent-encoding for URL parameters
Performance and Optimization Tips
Optimize Base64 usage for better application performance:
Performance Best Practices:
- Use Base64 for small files (<10KB) to reduce HTTP requests
- Serve large images as separate files with caching headers
- Consider WebP format before Base64 encoding images
- Use streaming for large Base64 operations
- Implement client-side caching for repeated Base64 operations
- Consider gzip compression for Base64 text content
Frequently Asked Questions
Related Articles
Learn More About Base64 Encoder Decoder Guide
A free online Base64 Encoder Decoder Guide tool.
This tool is designed to be simple, fast, and effective. Whether you are a professional or just need a quick solution, Base64 Encoder Decoder Guide is here to help. We continuously update our tools to ensure accuracy and better user experience.
Related Tools
HTML to Markdown
Convert HTML code to Markdown format for easier editing.
Word Counter
Count words, characters, sentences, and paragraphs in your text.
Pounds to Kg Converter
Convert pounds to kilograms and vice versa. Essential for fitness, health, and international weight measurements.
CSS Minifier
Minify CSS code to reduce file size and improve load times.