Ultimate Guide to Image Optimization in 2025
Speed up your website by up to 40% with advanced image optimization techniques and next-gen formats
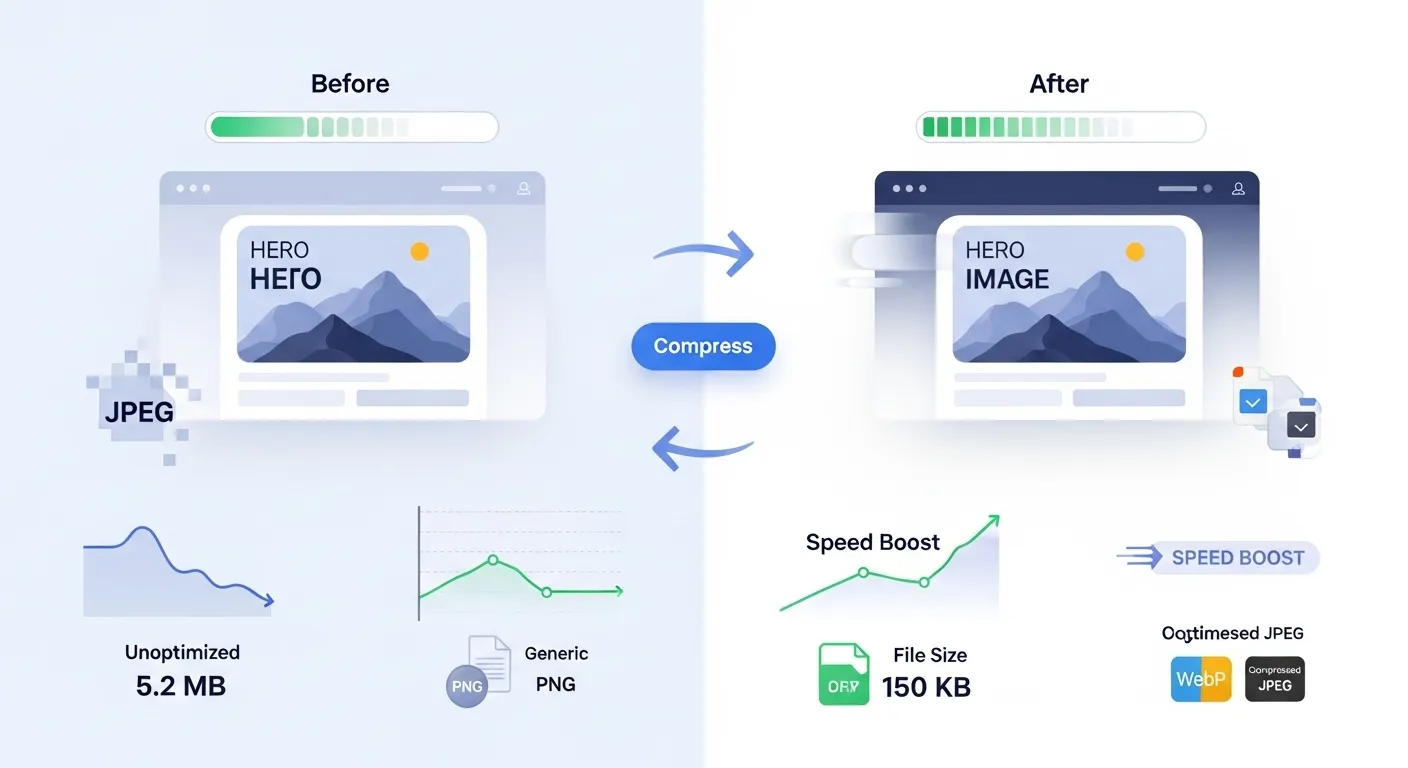
Why Image Optimization Matters
Images often account for 60-70% of a website's total file size. Optimizing your images can dramatically improve your site's loading speed, user experience, and search engine rankings.
Understanding Image Formats
JPEG/JPG
Best for photographs and complex images with many colors. Uses lossy compression.
- Small file sizes
- Wide browser support
- No transparency
PNG
Perfect for graphics, logos, and images requiring transparency. Uses lossless compression.
- Transparency support
- Lossless quality
- Larger file sizes
WebP
Modern format offering superior compression. 25-35% smaller than JPEG with same quality.
- Excellent compression
- Transparency support
- Limited older browser support
AVIF
Next-generation format with even better compression than WebP. Still gaining browser support.
- Best compression
- High quality
- New format, limited support
Compression Techniques
Lossy vs Lossless Compression
Lossy Compression
Reduces file size by permanently removing some image data. Used in JPEG format.
- Smaller file sizes
- Some quality loss
- Best for photos
Lossless Compression
Reduces file size without losing any image quality. Used in PNG format.
- Larger file sizes
- No quality loss
- Best for graphics
Quality Settings Guide
| Quality Level | Use Case | File Size | Visual Quality |
|---|---|---|---|
| 90-100% | Print, Professional Photography | Large | Excellent |
| 70-89% | Web Images, Social Media | Medium | Good |
| 50-69% | Thumbnails, Preview Images | Small | Acceptable |
| 10-49% | Placeholders, Low Priority Images | Very Small | Poor |
Optimization Best Practices
1. Choose the Right Dimensions
Never use CSS to resize images. Always resize images to their display dimensions before uploading.
2. Compress Before Upload
Always compress images before uploading them to your website. Use tools like our Image Compressor.
3. Use Modern Formats
Implement WebP with JPEG fallbacks for better compression and browser compatibility.
<picture>
<source srcset="image.webp" type="image/webp">
<img src="image.jpg" alt="Description">
</picture>4. Implement Lazy Loading
Load images only when they're about to enter the viewport to improve initial page load speed.
<img src="image.jpg" loading="lazy" alt="Description">Free Image Optimization Tools
Measuring Performance Impact
Use these tools to measure how image optimization affects your website performance:
-
Google PageSpeed InsightsAnalyze your page speed and get optimization suggestions
-
GTmetrixDetailed performance analysis with waterfall charts
-
Our Page Speed CheckerQuick performance analysis tool
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Don't Make These Mistakes
- Using uncompressed images straight from cameras
- Relying only on CSS for image resizing
- Not providing alt text for accessibility
- Using the wrong format for the image type
- Ignoring mobile optimization
- Not implementing lazy loading for below-fold images
Conclusion
Image optimization is crucial for website performance, user experience, and SEO. By choosing the right formats, compressing images appropriately, and implementing modern loading techniques, you can significantly improve your site's speed and user satisfaction.
Quick Checklist:
- Resize images to display dimensions
- Choose appropriate format (JPEG for photos, PNG for graphics)
- Compress images before upload
- Implement lazy loading
- Use modern formats like WebP when possible
- Test performance impact
How to Use Image Optimization Guide
- Input Data: Enter or paste your data into the input field.
- Process: The tool will automatically process your input or click the action button.
- View Results: See the results instantly and copy them if needed.
Common Use Cases
Professional Use
Perfect for developers, designers, and digital marketers who need quick results.
Education
Great for students and teachers for learning and verification.
Personal Projects
Simplify your personal tasks with this easy-to-use tool.
Everyday Tasks
Save time on routine calculations and conversions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Learn More About Image Optimization Guide
A free online Image Optimization Guide tool.
This tool is designed to be simple, fast, and effective. Whether you are a professional or just need a quick solution, Image Optimization Guide is here to help. We continuously update our tools to ensure accuracy and better user experience.