Image Metadata Explained
Understanding EXIF data, privacy implications, and optimization benefits of image metadata
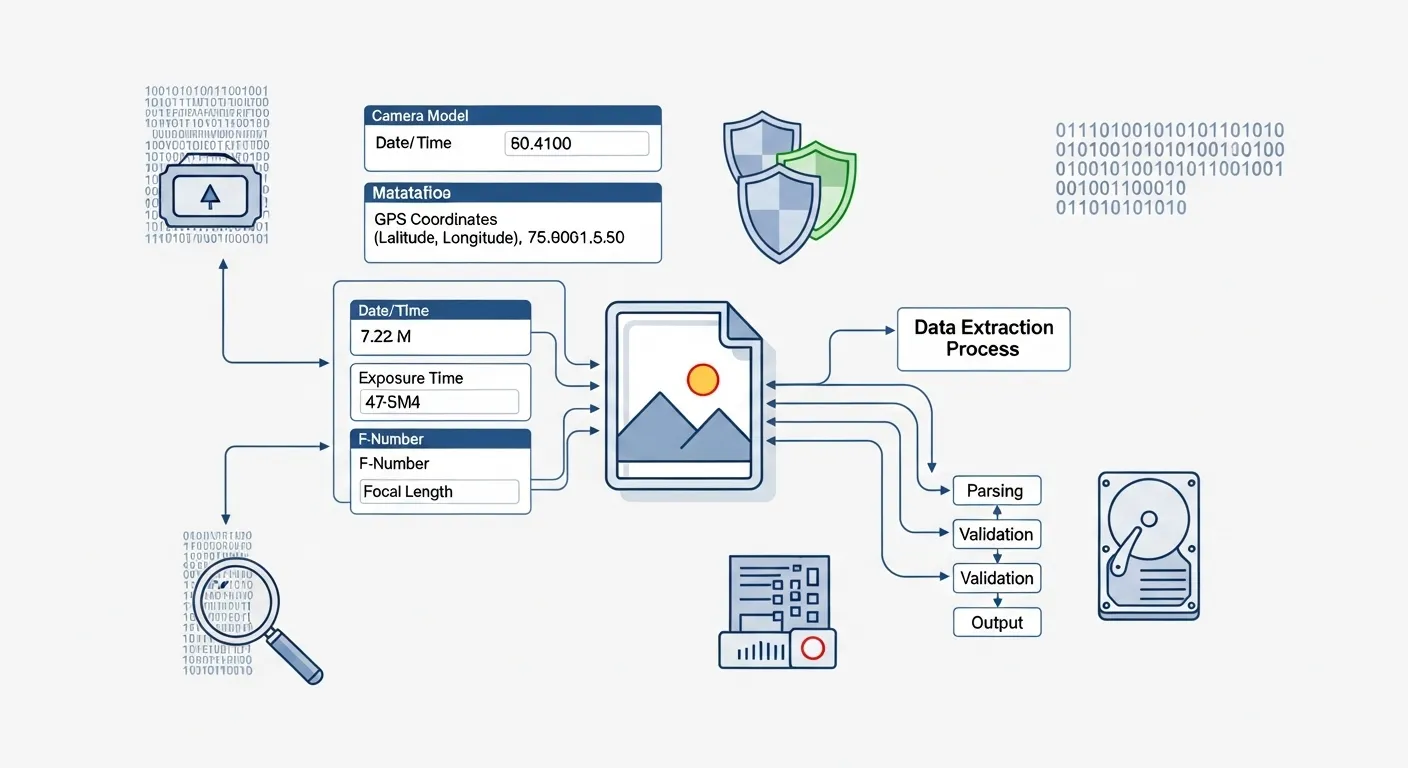
What is Image Metadata?
Image metadata is additional information embedded within image files that describes various aspects of the image, including camera settings, location data, timestamps, and technical details. This data is invisible when viewing the image but can be accessed by software and potentially by anyone who downloads the file.
Hidden Information
Data stored within the image file
Camera Details
Settings and equipment information
Location Data
GPS coordinates and location info
Types of Image Metadata
EXIF Data (Exchangeable Image File Format)
The most common type of metadata, automatically added by digital cameras and smartphones.
Camera Settings:
- Aperture (f-stop)
- Shutter speed
- ISO sensitivity
- Focal length
- Flash settings
- White balance
Device Information:
- Camera make and model
- Lens information
- Serial numbers
- Firmware version
- Software used
- Date and time
GPS/Location Data
Geographic information automatically added by smartphones and GPS-enabled cameras.
Location Information:
- Latitude coordinates
- Longitude coordinates
- Altitude/elevation
- Direction facing
- Speed (if moving)
- Your home address
- Work location
- Travel patterns
- Personal habits
- Sensitive locations
Color Profile & Technical Data
Information about color spaces, image processing, and technical specifications.
Color Information:
- Color space (sRGB, Adobe RGB)
- Color profile
- Gamma correction
- Rendering intent
Technical Details:
- Image dimensions
- Resolution (DPI)
- Bit depth
- Compression settings
User-Added Metadata
Information manually added by users or software applications.
Descriptive Data:
- Title and description
- Keywords/tags
- Author/photographer
- Copyright information
Software Data:
- Editing software used
- Processing history
- Thumbnail images
- Version information
Privacy and Security Implications
Security Risks
Sharing images with metadata can expose sensitive information:
- Location tracking: GPS data reveals where photos were taken
- Personal patterns: Timestamps show your daily routines
- Equipment details: Expensive camera info may attract thieves
- Identity exposure: Camera serial numbers can be traced
- Professional secrets: Camera settings reveal techniques
Real-World Privacy Scenarios
❌ High Risk Scenarios
- • Photos of your home or workplace
- • Images shared on social media
- • Photos of children or family
- • Travel photos from private locations
- • Professional work samples
✅ Lower Risk Scenarios
- • Stock photography
- • Public event photos
- • Landscape photography
- • Product images
- • Generic illustrations
Web Performance Impact
File Size Impact
Metadata can significantly increase file sizes, especially for web-optimized images.
| Metadata Type | Typical Size | Impact on Small Images | Performance Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic EXIF | 2-10 KB | 10-30% increase | Moderate |
| GPS Data | 1-3 KB | 5-15% increase | Low |
| Color Profiles | 3-50 KB | 15-100% increase | High |
| Thumbnails | 5-20 KB | 20-50% increase | High |
| Software History | 1-5 KB | 5-20% increase | Low-Moderate |
Loading Speed Impact
- • Slower page load times
- • Increased bandwidth usage
- • Poor mobile performance
- • Higher data costs for users
SEO Considerations
- • Page speed affects rankings
- • Core Web Vitals impact
- • Mobile-first indexing
- • User experience signals
When to Keep vs Remove Metadata
Keep Metadata When:
- Archiving personal photos
- Professional photography portfolios
- Stock photography submissions
- Legal documentation needs
- Copyright protection
- Technical analysis required
- Educational purposes
Remove Metadata When:
- Publishing on websites
- Sharing on social media
- Sending via email
- Privacy is a concern
- Optimizing for web performance
- Reducing file sizes
- Commercial use
How to View Image Metadata
Windows
- Right-click on image file
- Select "Properties"
- Click "Details" tab
- View EXIF information
macOS
- Open image in Preview
- Go to Tools menu
- Select "Show Inspector"
- Click "EXIF" tab
Mobile Apps
- • Photo Investigator (iOS)
- • EXIF Viewer (Android)
- • ViewExif (iOS/Android)
- • Photo Metadata (Android)
Online Tools
- • Jeffrey's Image Metadata Viewer
- • Metapicz.com
- • Exifdata.com
- • Our Image Metadata Viewer
How to Remove Image Metadata
Automatic Removal Tools
Manual Removal Methods
Desktop Software
- Adobe Photoshop: File > Export > Export As (uncheck metadata)
- GIMP: File > Export As (advanced options)
- ExifTool: Command-line metadata editor
- IrfanView: Image > Information > Remove
Mobile Methods
- iOS: Use Shortcuts app to strip EXIF
- Android: Photo Metadata Remover app
- Screenshot method: Take screenshot of image
- Social media: Platforms often strip metadata
Best Practices for Metadata Management
Privacy-First Approach
✅ Do:
- Review metadata before sharing
- Strip metadata for web use
- Disable GPS on camera/phone when needed
- Use tools that automatically remove metadata
- Keep original files with metadata separately
❌ Don't:
- Share images with GPS data publicly
- Ignore metadata in sensitive photos
- Assume social media strips all metadata
- Share images with personal information
- Forget to check downloaded images
Web Optimization Workflow
- Assess the image purpose - Determine if metadata is needed
- Check current metadata - Use tools to view existing data
- Remove unnecessary data - Strip privacy-sensitive information
- Optimize for web - Compress and resize as needed
- Verify removal - Double-check that metadata is gone
- Test performance - Measure file size improvements
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Important Legal Points
- Copyright information: Removing copyright metadata may violate laws
- Evidence preservation: Metadata may be crucial for legal cases
- Professional requirements: Some industries require metadata retention
- Attribution rights: Photographer credits in metadata should be respected
- Privacy laws: GDPR and similar regulations may apply to metadata
Conclusion
Image metadata serves important purposes but can pose privacy risks and performance issues when sharing images online. Understanding what metadata contains and how to manage it appropriately is essential for both privacy protection and web optimization.
Metadata Management Checklist:
- Understand what metadata your images contain
- Remove sensitive data before sharing
- Use tools that automatically strip metadata
- Consider performance impact on websites
- Preserve metadata for archival purposes
- Respect copyright and attribution data
- Configure devices to limit metadata creation
- Regularly audit your metadata practices
How to Use Image Metadata Explained
- Input Data: Enter or paste your data into the input field.
- Process: The tool will automatically process your input or click the action button.
- View Results: See the results instantly and copy them if needed.
Frequently Asked Questions
Learn More About Image Metadata Explained
A free online Image Metadata Explained tool.
This tool is designed to be simple, fast, and effective. Whether you are a professional or just need a quick solution, Image Metadata Explained is here to help. We continuously update our tools to ensure accuracy and better user experience.